-
Home
- About Us
- Product Center
-
Reverse osmosis equipment
-
Ultra pure water EDI equipment
-
Fully automatic softening water equipment
-
Multi medium filter
-
Ultrafiltration equipment
- Honorary qualifications
- application area
- News and information
Inquiry
Contact UsIf you have any questions, please contact us immediately!Water and liquid purification manufacturing
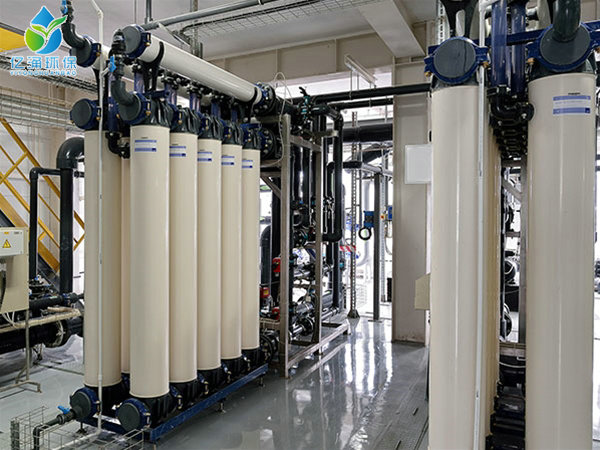
- Type:Ultrafiltration equipment
- Code:

-
Ultrafiltration is a separation process that utilizes a microporous screening mechanism of a pressure activated membrane to retain colloids, particles, and substances with relatively high amounts of solutes in water under external driving forces (pressure), while water and small solute particles pass through the membrane. Materials with a molecular weight of 3x10000-1x10000 can be intercepted through the screening of micropores on the membrane surface. When the treated water passes through the membrane surface at a certain flow rate with the help of external pressure, water molecules and solutes with a water treatment particle size of less than 300-500 pass through the membrane, while particles and macromolecules larger than the membrane pores are intercepted due to sieving, thus purifying the water. After passing through the ultrafiltration membrane, most of the colloidal silicon in the water can be removed, and a large amount of organic matter can also be removed. Ultrafiltration equipment can effectively remove impurities such as suspended solids, colloids, organic macromolecules, bacteria, microorganisms, etc. from water. Due to its excellent filtration performance, ultrafiltration is widely used in various water treatment systems.
- Product Description
Ultrafiltration is a separation process that utilizes a microporous screening mechanism of a pressure activated membrane to retain colloids, particles, and substances with relatively high amounts of solutes in water under external driving forces (pressure), while water and small solute particles pass through the membrane. Materials with a molecular weight of 3x10000-1x10000 can be intercepted through the screening of micropores on the membrane surface. When the treated water passes through the membrane surface at a certain flow rate with the help of external pressure, water molecules and solutes with a water treatment particle size of less than 300-500 pass through the membrane, while particles and macromolecules larger than the membrane pores are intercepted due to sieving, thus purifying the water. After passing through the ultrafiltration membrane, most of the colloidal silicon in the water can be removed, and a large amount of organic matter can also be removed. Ultrafiltration equipment can effectively remove impurities such as suspended solids, colloids, organic macromolecules, bacteria, microorganisms, etc. from water. Due to its excellent filtration performance, ultrafiltration is widely used in various water treatment systems.
Copyright @ 2024 . All rights reservedDezhou Yichong Environmental Protection Equipment Co., Ltd 备案号:鲁ICP备2024083378号-1 技术支持 极速互联-
Hot wire
Hot wire
15932676960
-
wechat

-
TOP
- 本区域为共用内容,已被锁定!如需修改,请选择右上角的解锁键。
- About Us